Historical Milestones
No other city has a richer history of international cooperation than Geneva.
In 1863, a small group of Genevois created the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) which led to the first international humanitarian treaty, the Geneva Convention of 1864.
In 1919, the city gained strength and momentum as a platform for dialogue and cooperation when the victorious states of World War I decided to establish the League of Nations and the International Labour Organization (ILO) there.
After World War II, the international community chose Geneva again to host key international organizations. Today, key actors in the health sector, like the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria have all set up headquarters there.
Discover the timeline of International Geneva history.
-
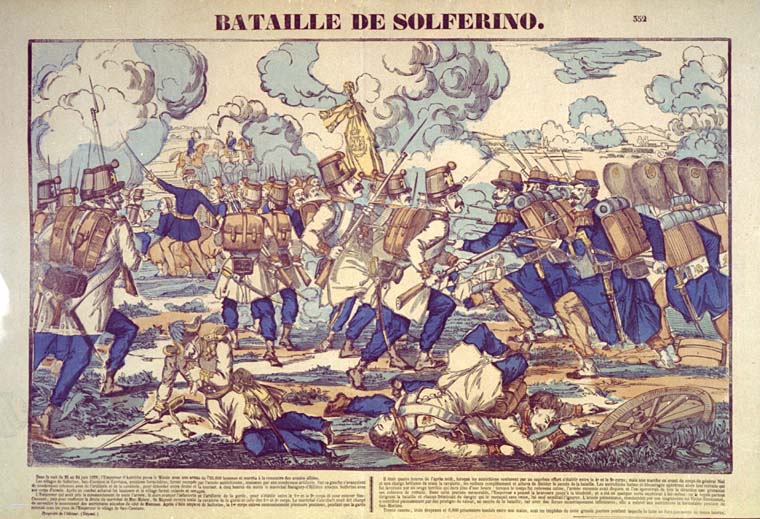
1859
The battle of Solferino was fought in northern Italy on 24 June 1859. A young Swiss man named Henry Dunant – who was in the area for business – did his best to care for the wounded and dying. This battle led Dunant to push for the creation of a neutral and impartial organization to protect and assist war victims (ICRC).
-
1925
The International Bureau of Education (IBE) is created in Geneva to centralize documentation related to public and private education, take an interest in scientific research in the educational field, and to serve as a coordinating centre for institutions and societies concerned with education.
-
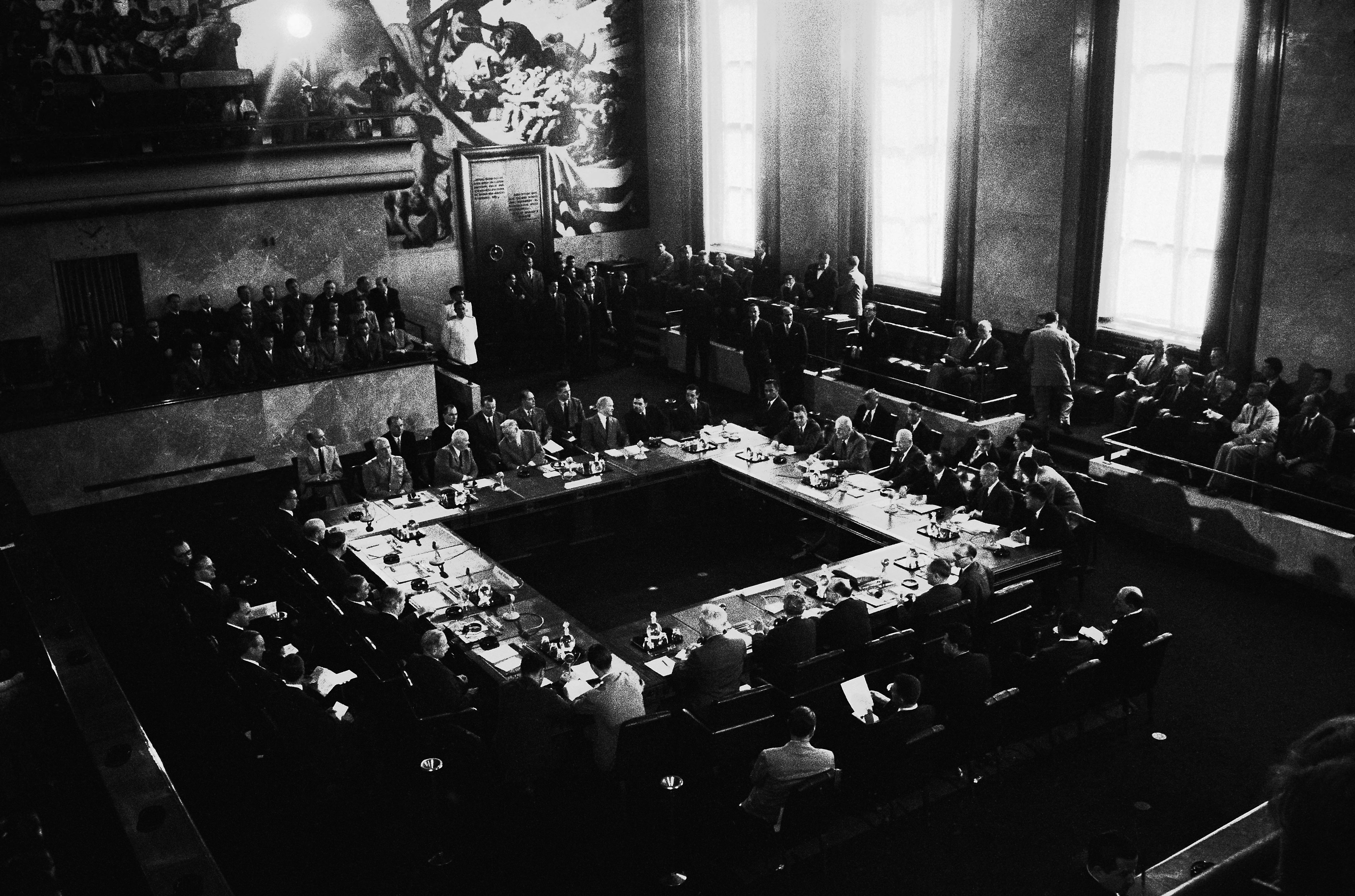
1949
The four Geneva Conventions are adopted. These international treaties lay at the core of international humanitarian law and protect those who are not taking part in the hostilities (civilians, health workers and aid workers) and those who are no longer participating in the hostilities, such as wounded, sick and shipwrecked soldiers and prisoners of war.
-
1955
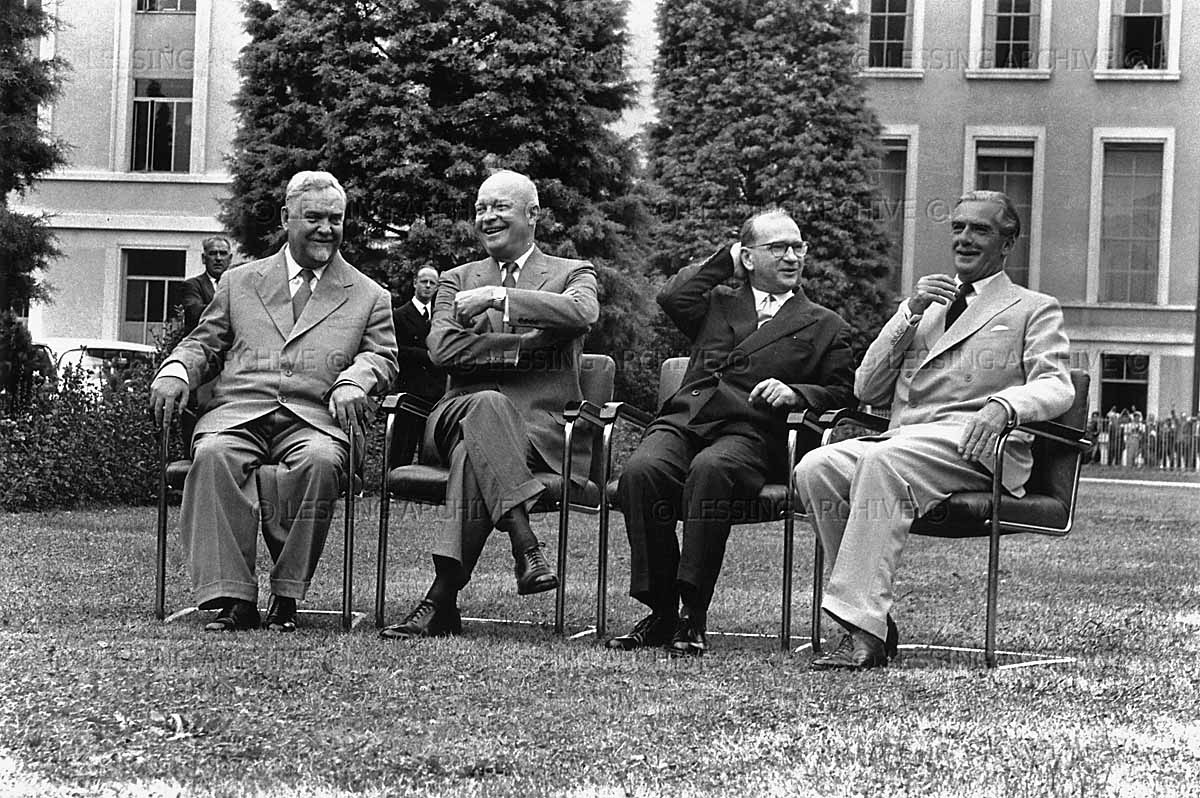
For the fist time since 1945, the winners of World War II - President Dwight D. Eisenhower for the United States, Prime Minister Anthony Eden for Britain, Premier Nikolai A. Bulganin for the Soviet Union, and Prime Minister Edgar Faure for France - meet in Geneva to discuss European security, disarmament and Germany's reunification.
-
1987
The Brundtland Report defines, for the first time, the concept of sustainable development by stating that development is sustainable “if it guarantees that the needs of the current generation are met, without prejudicing the ability of future generations to meet their needs”. The report is published by the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED), chaired by Gro Harlem Brundtland, a former Norwegian Prime Minister.
-
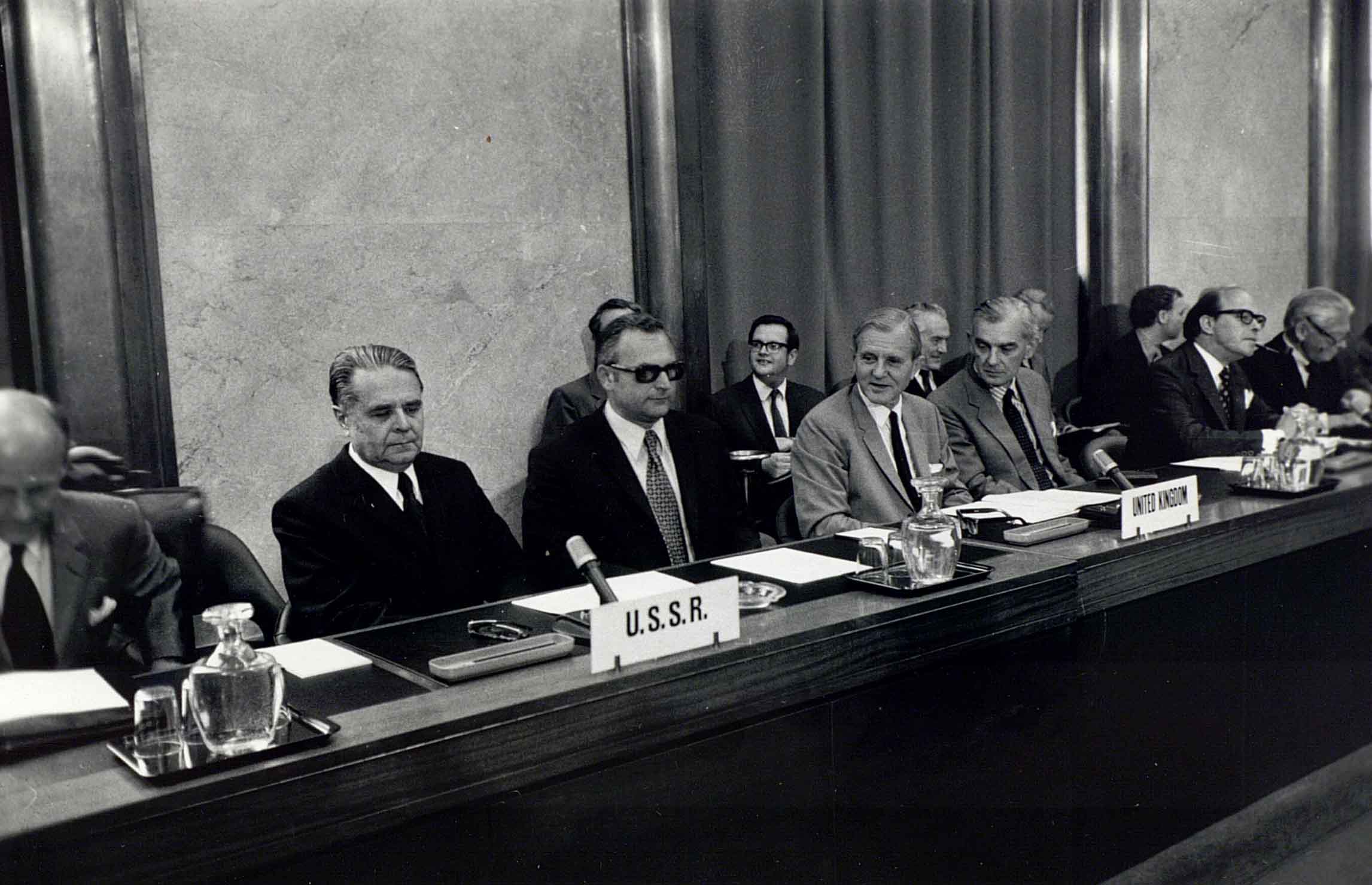
2000
The Gavi Alliance chooses Geneva for its headquarters. In the following years, most innovative partnerships in the health sector choose Geneva: the Global Fund to fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, the Roll Back Malaria Partnership (RBM), Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative (DNDi), Foundation for innovative new diagnosis (FIND), Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN), the Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV) and the Stop TB Partnership.